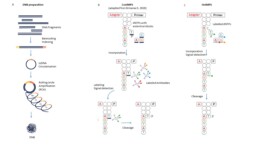
“Short read” sequencing by DNB
The technology proposed by MGI is based on the sequencing by synthesis (SBS) of single-stranded DNA (DNB). The preparation of the libraries involves circularization and replication (rolling circle replication) of previously indexed DNA/cDNA fragments to form DNBs of 300 to 500 copies for each fragment (Figure A ). This method avoids amplification bias and gives low duplicate and sequencing error rates.
Sequencing by synthesis (SBS) of DNBs has evolved from CoolMPS to HotMPS (Figure B,C).
In the first case, a dNTP carrying a specific 3′ blocking end is incorporated in each cycle. Fluorescent antibodies recognizing the different blocking groups allow the identification of the nucleotides. After cleavage of the complex blocking group-antibody, a new cycle can be started (see).
HotMPS uses the “standard” protocol with dNTP-H carrying 3′ blocking chromophores. After identification of the incorporated base by signal detection, cleavage of the chromophore by an H-enzyme releases the 3′ for further incorporation.
The reading of the complementary strand (paired end) uses the MDA system (Multiple Displacement Amplification- Dean FB 2002) .