ScNaUmi-seq
The conventional approach of scRNAseq is based on the sequencing of short fragments of indexed cDNAs (see scRNAseq). The analysis of “full length cDNAs” requires, therefore, a bioinformatics assembly process that complicates, for example, the detection of transcript isoforms. To overcome this, long-read sequencing using PacBio or Nanopore (ONT) technologies would be more appropriate.
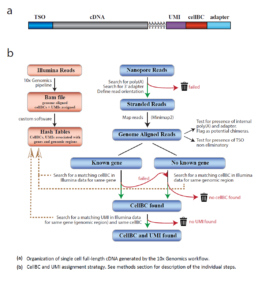
The ScNaUmi-seq method (Lebrigand et al. 2020) uses the same strategy as Dropseq for the capture and 3’end-indexing of RNApoly A (Figure) followed by Nanopore sequencing. Data processing, based on accurate assignment of cellBCs and UMIs, follows several steps (Figure) that reduce RT or PCR artifacts and identify true transcript chimeras and rare isoforms. The improvement of cDNA library preparation kits (Smart seq v4, ONT V14 kit, etc…), Nanopore chemistry and read analysis quality should facilitate cell transcriptome profiling (cf Nanopore 2022)