Mapping of DNA-protein interaction sites: CHIP seq
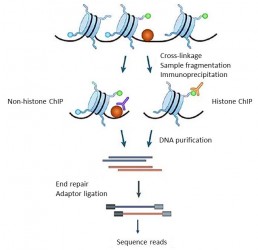
Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation Sequencing is a methodology used to analyze the DNA-proteins interactions. This technology combines chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), using antibodies specific to a protein of interest and high throughput sequencing.
ChIP enables the mapping of all DNA binding sites of a protein of interest at the genome level. For example, it is possible to identify each genomic region associated with a nucleosomal histone carrying a biochemical modification (acetylation, methylation, etc.) typical of transcription activity, or to define transcription factors binding sites (PJ Park et al. 2009).
The principle of the methodology consists in covalently binding DNA-bound proteins by chemical process, fragmenting chromatin, isolating DNA-protein complexes by immunoprecipitation in the presence of the antibody of interest. After protein depletion and purification, the DNA fragments collected are sequenced.
Rubriques associées
- Small RNA Sequencing
- Mapping of Transcription Start Sites – TSS
- TAPS/TAPSβ
- Enzymatic Methyl-seq (EM-seq™)
- Methylation of native DNA and RNA
- DNA binding sites map : CUT & RUN vs CUT & Tag
- Chromosome Contact map : 3C, 4C , 5C
- High Chromosome Contact map : HiC-seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: DNase seq
- Indirect mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: MNase seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: FAIRE seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: ATAC seq
- Mapping of RNA-protein interaction sites: CLIP seq
- Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: MeDIP
- Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: Methyl seq
- BiSeq