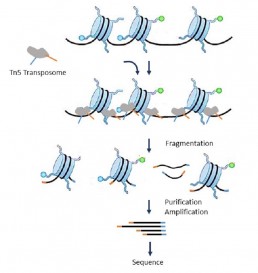
Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: ATAC seq
ATAC seq (Assay for transposase accessible chromatin) is an interesting methodology for identifying open chromatin regions, ascertaining positions with or without nucleosomes in regulatory regions, and analyzing the occupancy of transcription factors (TFs) in specific cell types. Thus, this application can generate fairly complete epigenomic profiles.
The principle of the technique consists in incubating the chromatin with Tn5 transposomes to simultaneously fragment and index the exposed DNA fragments (J Buenrostro et al. 2015). However, this simple and time-saving protocol must be carried out carefully in order not to modify the structure of the chromatin revealing sites to the transposomes.
Rubriques associées
- Small RNA Sequencing
- Mapping of Transcription Start Sites – TSS
- TAPS/TAPSβ
- Enzymatic Methyl-seq (EM-seq™)
- Methylation of native DNA and RNA
- DNA binding sites map : CUT & RUN vs CUT & Tag
- Chromosome Contact map : 3C, 4C , 5C
- High Chromosome Contact map : HiC-seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: DNase seq
- Indirect mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: MNase seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: FAIRE seq
- Mapping of RNA-protein interaction sites: CLIP seq
- Mapping of DNA-protein interaction sites: CHIP seq
- Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: MeDIP
- Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: Methyl seq
- BiSeq