High Chromosome Contact map : HiC-seq
The study of the 3D conformation of the chromatin and the cis (intra chromosome) and trans (inter chromosome) interactions allows the identification of topological domains (TADs). TADs are not only structural compartments of chromatin but also regions of DNA replication and genome regulation (Lupiáñez et al. 2015).
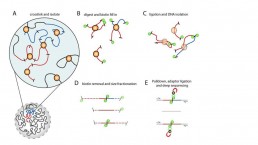
The HiC-seq method is based on the capture of the chromatin conformation and the sequencing of the regions of chromosome interaction, providing a picture of the activity of the TADs at a given time.
The chromatin is immobilised in its 3D conformation with formaldehyde (crosslinking). The DNA is fragmented by enzymatic digestion (HindIII), the sticky ends of the restriction sites are filled in with biotinylated nucleotides. After ligation of the new blunt ends, purification on streptavidin beads is used to specific isolate of the DNA of chromosome interaction regions.
Rubriques associées
- Small RNA Sequencing
- Mapping of Transcription Start Sites – TSS
- TAPS/TAPSβ
- Enzymatic Methyl-seq (EM-seq™)
- Methylation of native DNA and RNA
- DNA binding sites map : CUT & RUN vs CUT & Tag
- Chromosome Contact map : 3C, 4C , 5C
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: DNase seq
- Indirect mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: MNase seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: FAIRE seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: ATAC seq
- Mapping of RNA-protein interaction sites: CLIP seq
- Mapping of DNA-protein interaction sites: CHIP seq
- Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: MeDIP
- Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: Methyl seq
- BiSeq