BiSeq
DNA methylation is one of the most studied epigenetic modifications because it plays an important role in regulating gene expression and therefore influences both many biological processes and a wide range of diseases.
Thanks to new generation sequencing technologies (NGS), the study of methyloma is possible on the whole genome with a resolution at the base pair level.
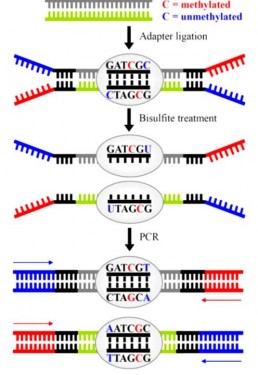
The BiSeq technique (Bisulfite sequencing) is based on the treatment of ssDNA with sodium bisulfite which deaminates non-methylated C (C) faster than methylated C (5mC and 5hmC). This treatment, which converts C to Uracil and then to T after amplification (Fig1), transforms the epigenetic mark into an genetic variation identified by sequencing (WS Yong et al. 2016) .
The BiSeq protocol consists of preparing DNA fragments by sonication, indexing them with methylated adapters and then selecting them by size. The libraries are then treated with sodium bisulfite, amplified and sequenced. The conversion reaction can be checked by integrating non-methylated control DNA, knowing that excessive incubation time or inadequat bisulfite/DNA ratio not only denatures the DNA but also can modify the methylated Cs and thereby can underestimate the methylation status of the sample (PW Laird. 2010).
BiSeq data analysis is tricky because the conversion creates a C=>T transition on each position of each DNA strand. For each sequenced locus, must be aligned the “G-rich” strand, its “C-rich” complementary strand, the “T-rich” converted strand and its “A-rich” complementary strand (Fig1) . To help en this issue, the “BiSeqS” method introduces molecular barcoding in order to discriminate the methylation state of each of the 2 DNA (AK Mattox et al. 2017) .
Rubriques associées
- Small RNA Sequencing
- Mapping of Transcription Start Sites – TSS
- TAPS/TAPSβ
- Enzymatic Methyl-seq (EM-seq™)
- Methylation of native DNA and RNA
- DNA binding sites map : CUT & RUN vs CUT & Tag
- Chromosome Contact map : 3C, 4C , 5C
- High Chromosome Contact map : HiC-seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: DNase seq
- Indirect mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: MNase seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: FAIRE seq
- Mapping of chromatin accessibility sites: ATAC seq
- Mapping of RNA-protein interaction sites: CLIP seq
- Mapping of DNA-protein interaction sites: CHIP seq
- Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: MeDIP
- Mapping of DNA epigenetic marks: Methyl seq